

Rat prostatitis model

01. Background:
Prostatitis refers to acute or chronic inflammation caused by specific and nonspecific infection of the prostate, which can cause systemic or local symptoms. The establishment of an animal model of prostatitis provides a basis for further etiological research and the development of new specific drug treatments. This article details the experimental materials, methods, and verification methods for establishing a rat prostatitis model by injecting estradiol benzoate.
02. Experimental materials and methods
Experimental materials: SD rats (male, 240-300 g); estradiol benzoate
Modeling method:
1. Rats were anesthetized with 2-3% isoflurane, fixed after anesthesia and coma, all abdominal hair was removed, iodine disinfection was performed, the abdomen was opened, and the testicles were removed.
2. After surgery, estradiol benzoate (0.25 mg/kg, dissolved in soybean oil) was injected subcutaneously once a day for 4 consecutive weeks.
3. Samples were collected 4 weeks after modeling, and HE staining was used to observe prostate interstitial congestion, edema, and inflammatory cell infiltration in the interstitium.
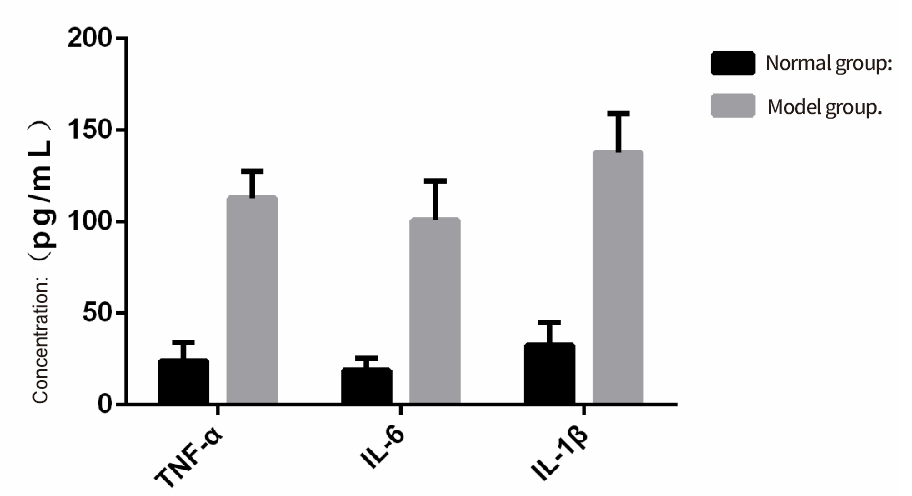
Evaluation indicators: serum inflammatory factor detection, HE staining.
03. Certification
Serum Inflammatory Factor ELISA Assay
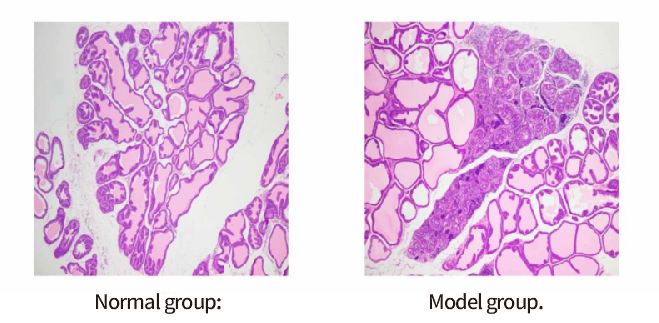
HE staining
HE staining results: compared with the normal group, the histopathy was obvious, with abnormal tissue structure, widening of the prostate interstitium, irregular morphology of some glandular lumen, a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrating the gland and interstitium, and disorganized and hyperplastic arrangement of glandular epithelial cells.
Indicators related to prostatitis are as follows



