

Direct access to Sepsis
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome caused by infectious factors, which can lead to organ dysfunction and circulatory disorders in severe cases. It is also a common complication of severe trauma, burns, shock, infection and major surgical operations, with a high mortality rate. Sepsis and its related complications are still prominent problems facing critical care medicine today. The establishment of animal disease models can help people better explore the pathogenesis of sepsis and find effective treatment measures, obtain earlier diagnosis and take intervention measures.
Currently, more than 100 markers for sepsis have been proposed, and determining which markers are helpful in optimizing diagnostic and treatment strategies.
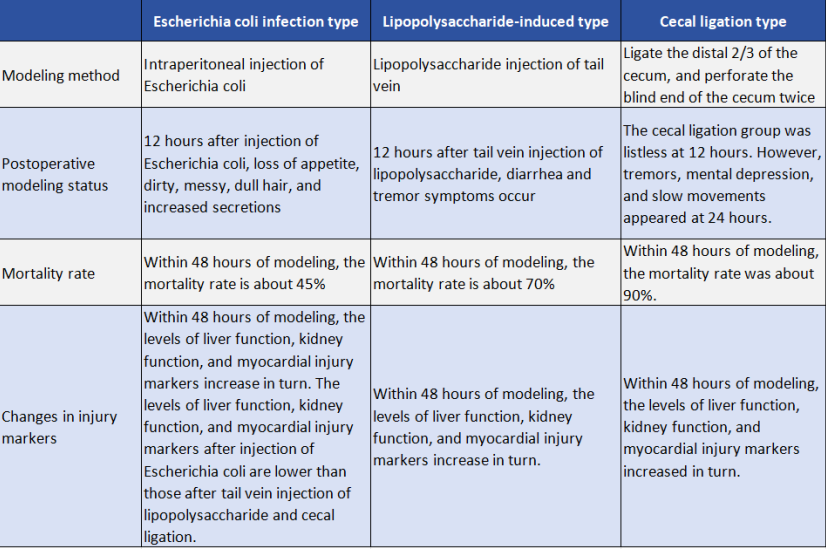
There are three main methods for sepsis modeling, including Escherichia coli infection, lipopolysaccharide-induced, and cecal ligation.
Ⅰ. Traditional infection-related biomarkers
1. Procalcitonin (PCT) PCT is the most studied infection-related inflammatory marker in the past 10 years. It is a glycoprotein composed of 116 amino acids that is released by cells stimulated by bacterial infection.
2. C-reactive protein (CRP) CRP is one of the most commonly used clinical biomarkers for early diagnosis of sepsis and is also a widely used inflammatory indicator in clinical practice. It has high sensitivity but lacks specificity.
3. Cytokines Overactivation of inflammatory cells and release of a large number of inflammatory cytokines is one of the important mechanisms of sepsis. Currently, cytokines such as TNFα, IL-6, IL-1β, etc., which are used as markers, have been repeatedly mentioned and compared in the literature, proving that they have certain advantages in the diagnosis of sepsis.
Ⅱ. Markers related to inflammatory response activation and immune imbalance
1. Calprotectin Studies have found that the expression level of calprotectin is significantly increased in sepsis (the serum calprotectin concentration of normal people is usually less than 1 mg/L, and it can increase 100 times in sepsis.)
2. Serum penetrant 3 (PTX3) PTX3 is an acute phase protein belonging to the long-chain pentraxin. Under the stimulation of inflammatory cytokines, all kinds of immune cells, endothelial cells and epithelial cells secrete PTX3.
3. Soluble CD14 subtype (Presepsin) CD14 exists in two forms, namely membrane-bound form (mCD14) and soluble form (sCD14). sCD14 has different subtypes, and the N-terminal fragment of sCD14 is called Presepsin. When infected by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, the level of Presepsin in serum increases sharply, which can be used as one of the new biomarkers for the diagnosis and detection of sepsis.
4. Monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) Studies have shown that the plasma MCP-1 level in patients with sepsis is directly correlated with the levels of other cytokines and is a potential biomarker for predicting the development of sepsis.
5. Toll receptor (TLR4) Studies have shown that the expression of TLRs such as TLR2 and TLR4 in patients with sepsis increases sharply, activates NFκB, releases a large number of inflammatory factors, and can induce sepsis.
6. Soluble tumor necrosis factor type I receptor (sTNFR1) In sepsis, TNF release increases, and two TNF membrane-bound receptors TNFR1 and TNFR2 are released into the circulation to regulate the inflammatory response.
Sepsis markers related products recommended
|
Product Name |
Cat No |
|
Mouse PCT(Procalcitonin) ELISA Kit |
ELK4534 |
|
Rat PCT(Procalcitonin) ELISA Kit |
ELK3983 |
|
Human PCT(Procalcitonin) ELISA Kit |
ELK1088 |
|
Mouse CRP(C Reactive Protein) ELISA Kit |
ELK1056 |
|
Rat CRP(C Reactive Protein) ELISA Kit |
ELK1055 |
|
Human CRP(C Reactive Protein) ELISA Kit |
ELK1040 |
|
Rat TNFa(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
ELK1396 |
|
Mouse TNFa(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
ELK1387 |
|
Mouse TNFa(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
ELK1395 |
|
Human TNFa(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
ELK1190 |
|
Human IL1b(Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit |
ELK1270 |
|
Rat IL1b(Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit |
ELK1272 |
|
Mouse IL1b(Interleukin 1 Beta) ELISA Kit |
ELK1271 |
|
Rat IL6(Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
ELK1158 |
|
Mouse IL6(Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
ELK1157 |
|
Human IL6(Interleukin 6) ELISA Kit |
ELK1156 |
|
Mouse CALP(Calprotectin) ELISA Kit |
ELK9617 |
|
Rat CALP(Calprotectin) ELISA Kit |
ELK9259 |
|
Human CALP(Calprotectin) ELISA Kit |
ELK4602 |
|
Mouse PTX3(Pentraxin 3, Long) ELISA Kit |
ELK7332 |
|
Rat PTX3(Pentraxin 3, Long) ELISA Kit |
ELK6256 |
|
Human PTX3(Pentraxin 3, Long) ELISA Kit |
ELK3268 |
|
Mouse sCD14(SolubleCluster of Differentiation 14) ELISA Kit |
ELK9619 |
|
Human sCD14(soluble cluster of differentiation 14) ELISA Kit |
ELK8435 |
|
Rat MCP1(Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1) ELISA Kit |
ELK5504 |
|
Human MCP1(Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1) ELISA Kit |
ELK5252 |
|
Mouse MCP1(Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1) ELISA Kit |
ELK5056 |
|
Mouse TLR4(Toll Like Receptor 4) ELISA Kit |
ELK2665 |
|
Rat TLR4(Toll Like Receptor 4) ELISA Kit |
ELK2106 |
|
Human TLR4(Toll Like Receptor 4) ELISA Kit |
ELK1777 |
[1] Wang Jing, Qiao Youjie. Research progress of sepsis related biomarkers [J]. Journal of Refractory Diseases, 2019,22(05):540-545. (in Chinese)


