Explanation of cytokines: the interleukin family

1, The Past and present Life of interleukin
There is a group of protein molecules in the human body that are unknown but play a vital role in the immune system. They are interleukins (IL), Interleukins are a type of lymphokine produced by a variety of cells and interacting between leukocytes or immune cells. They are not only a key link in immune regulation, but also play an important role in hematopoiesis, anti-tumor and other aspects. In the 1970s, researchers first discovered interleukins in leukocytes and named them IL-1. The IL-1 series of cytokines have the function of regulating cell signal transduction and promoting cell proliferation. Since then, researchers have found that IL-1 can also induce fever and promote inflammatory responses. This study laid the foundation for subsequent interleukin research. As the research deepened, scientists have discovered many new interleukins. According to their functional and structural differences, interleukins are divided into different types and numbered in the form of IL-n (positive integers).
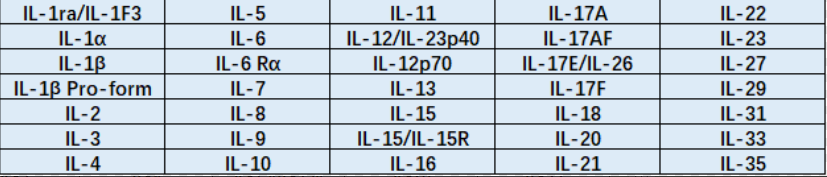
2, the main function of interleukin
The main functions of interleukins include but are not limited to the following aspects:
1) Immunomodulation: Interleukins play a core role in the regulation of immune responses. They can promote or inhibit the proliferation, differentiation and activation of immune cells, thereby regulating the intensity and direction of immune responses. For example, some interleukins (such as IL-2, IL-12) can stimulate the proliferation and activation of T cells and NK cells (natural killer cells) and enhance cellular immune responses; while other interleukins (such as IL-4, IL-10) may inhibit the activation of immune cells, helping to prevent excessive immune responses and the occurrence of autoimmune diseases.
2) Inflammatory response: Interleukins can attract and activate other immune cells (such as neutrophils and monocytes) to the site of inflammation, promoting the occurrence and development of local inflammatory responses. At the same time, interleukins can also regulate the production and release of inflammatory mediators, further exacerbating or alleviating inflammatory responses
3) Hematopoietic effect: Some interleukins have an important effect on the hematopoietic system. They can promote the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells, regulate the generation and development of erythroid, granulocyte, megakaryocyte and other cells, thereby maintaining normal blood components and proportions.
4) Participation in tumor immunity: Interleukins also play an important role in anti-tumor immunity. They can activate the anti-tumor activity of immune cells (such as NK cells and macrophages) and directly kill tumor cells; they can also promote the recognition and attack of tumor cells by immune cells and enhance the body's immune surveillance and clearance of tumors.
5) Other functions: In addition to the above main functions, interleukins are also involved in many other physiological and pathological processes, such as tissue repair, metabolic regulation, and neuro-endocrine-immune network regulation. It should be emphasized that the functions of interleukins are complex and diverse. Different interleukins differ in structure and function. They interact and regulate with each other to jointly maintain the homeostasis and balance of the immune system. At the same time, due to the important role of interleukins in immune response, they have also become important targets for the treatment of many diseases (such as autoimmune diseases, tumors, infectious diseases, etc.).
3,Clinical application prospect of interleukin
The following are the specific application prospects of interleukins in the treatment of several types of diseases:
1) Autoimmune diseases Mechanism of action: Interleukins can regulate immune responses, inhibit cell proliferation, and promote cell differentiation and apoptosis, thereby alleviating excessive immune responses in autoimmune diseases. Application prospects: Interleukins can be used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. These diseases are usually accompanied by abnormal activation of the immune system, leading to attacks on one's own tissues. Interleukins help reduce inflammation and tissue damage by regulating immune responses.
2) Tumors Mechanism of action: Interleukins can activate immune cells, such as NK cells and macrophages, and enhance their ability to recognize and kill tumor cells. In addition, interleukins can promote apoptosis of tumor cells and inhibit their proliferation and metastasis. Application prospects: Interleukins have shown potential in the treatment of various tumors, such as renal cancer and melanoma. In particular, recombinant human interleukin-2 (IL-2), as an important bioactive polypeptide drug, has been widely used in the field of immunotherapy.
3) Rejection after organ transplantation Mechanism of action: After organ transplantation, the body's immune system may regard the transplanted organ as a foreign body and attack it, leading to rejection. Interleukins help alleviate this rejection by regulating the immune response. Application prospects: Interleukins can be used to prevent and treat rejection after organ transplantation, improve the survival rate of transplanted organs and the survival rate of patients.
4) Infectious diseases Mechanism of action: Interleukins play an important role in anti-infective immune responses and can enhance the body's resistance to pathogens. Application prospects: In the treatment of infectious diseases, interleukins can be used to enhance the body's anti-infective ability and improve the treatment effect. In addition, interleukins can also be used to treat septic shock, saving patients' lives by stabilizing the circulation state and improving organ function.
5) Anti-aging and other fields Latest research: It is worth noting that recent studies have shown that some interleukins (such as IL-11) also have potential in anti-aging. Anti-IL-11 treatment has been shown to delay aging, prolong life, and improve the health of elderly mice. Although research in this field is still in its early stages, it provides new ideas for future anti-aging treatments.
In summary, interleukins have shown important application prospects in many fields, including autoimmune diseases, tumors, rejection reactions after organ transplantation, infectious diseases, and anti-aging.
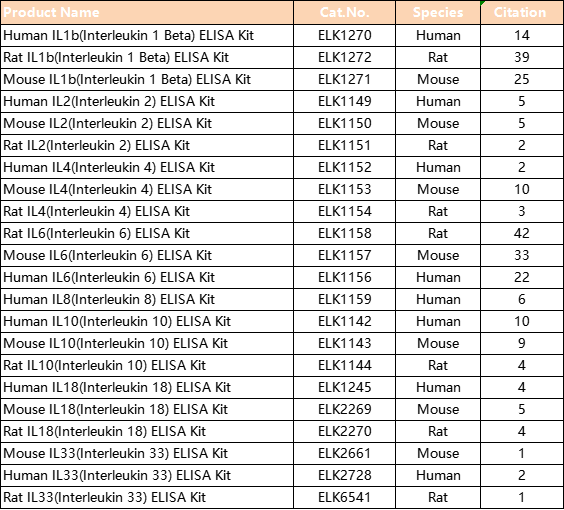
ELK Biotechnology products related to interleukin