

Clinical Applications of PCT
Respiratory infections account for approximately 10% of global morbidity and mortality. In conditions like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
2. Sepsis and Septicemia
For patients with suspected sepsis, measuring PCT concentration enables early diagnosis and initiation of critical treatment. A combined testing strategy—including blood culture, endotoxin, PCT, IL-6, and CRP—offers significant clinical value for the early prediction and diagnosis of severe septicemia.
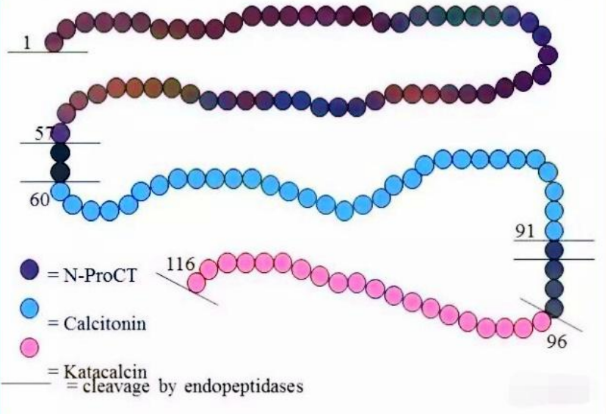
3. Oncological Diseases
Patients with hematological malignancies undergoing chemotherapy often develop neutropenia, significantly increasing their risk of infection. PCT levels rise during bacterial infections complicating chemotherapy and decrease with effective anti-infective treatment, making it a valuable tool for monitoring therapeutic response in oncology patients.
PCT is highly effective in distinguishing bacterial from viral or non infectious inflammatory conditions. For instance, PCT levels are significantly elevated in
PCT Detection with ELISA Kits
The measurement of PCT levels is efficiently performed using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) kits. These kits, as shown in the image below, contain all necessary components—including pre-coated plates, standards, and reagents—for accurate, high-throughput quantification of PCT in serum samples, supporting clinical diagnostics and research.
(Image: Professional layout of ELISA kits, reagents, and microplates used for PCT testing)
Summary


