





Rad21 rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | Rad21 rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse |
| Alternative Names: | RAD21; HR21; KIAA0078; NXP1; Double-strand-break repair protein rad21 homolog; hHR21; Nuclear matrix protein 1; NXP-1; SCC1 homolog |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. Immunofluorescence: 1/200 - 1/1000. ELISA: 1/5000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human RAD21. AA range:521-570 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 72kD |
| GeneID: | 5885 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | O60216 |
| Cellular localization: | [Double-strand-break repair protein rad21 homolog]: Nucleus . Nucleus matrix . Chromosome . Chromosome, centromere . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole . Associates with chromatin (PubMed:11590136, PubMed:11073952). Before prophase, scattered along chromosome arms (PubMed:11073952). During prophase and prometaphase, most cohesins dissociate from the arms of condensing chromosome, possibly through PLK1-mediated phosphorylation (PubMed:11931760). A small amount of cohesin remains in centromeric regions and is removed from chromosomes only at the onset of anaphase. At anaphase, cleavage by separase/ESPL1 leads to the dissociation of cohesin from chromosomes and chromosome separation (PubMed:11073952, PubMed:11509732). .; [64-kDa C-terminal product]: Cytoplasm, cytosol . Nucleus . |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to the gene product of Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad21, a gene involved in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks, as well as in chromatid cohesion during mitosis. This protein is a nuclear phospho-protein, which becomes hyperphosphorylated in cell cycle M phase. The highly regulated association of this protein with mitotic chromatin specifically at the centromere region suggests its role in sister chromatid cohesion in mitotic cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008], |
-
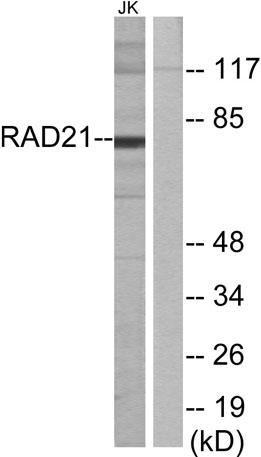
 Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat cells, using RAD21 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from Jurkat cells, using RAD21 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
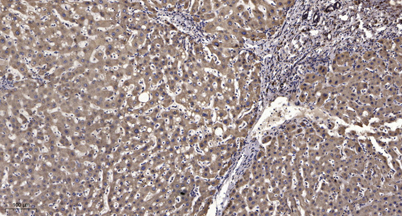
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).

 Manual
Manual