





PKD2 (phospho Ser812) rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | PKD2 (phospho Ser812) rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | PKD2; Polycystin-2; Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type II protein; Polycystic kidney disease 2 protein; Polycystwin; R48321 |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | WB 1:500-2000;IHC-p 1:50-300; ELISA 2000-20000 |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human PKD2 around the phosphorylation site of Ser812. AA range:778-827 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Molecular Weight: | 97kD |
| GeneID: | 5311 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | Q13563 |
| Cellular localization: | Cell projection, cilium membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Basolateral cell membrane . Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane . Golgi apparatus . PKD2 localization to the plasma and ciliary membranes requires PKD1. PKD1:PKD2 interaction is required to reach the Golgi apparatus form endoplasmic reticulum and then traffic to the cilia (By similarity). Retained in the endoplasmic reticulum by interaction with PACS1 and PACS2 (PubMed:15692563). Detected on kidney tubule basolateral membranes and basal cytoplasmic vesicles (PubMed:10770959). Cell surface and cilium localization requires GANAB (PubMed:27259053). . |
| Background: | polycystin 2, transient receptor potential cation channel(PKD2) Homo sapiens This gene encodes a member of the polycystin protein family. The encoded protein is a multi-pass membrane protein that functions as a calcium permeable cation channel, and is involved in calcium transport and calcium signaling in renal epithelial cells. This protein interacts with polycystin 1, and they may be partners in a common signaling cascade involved in tubular morphogenesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type 2. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011], |
-
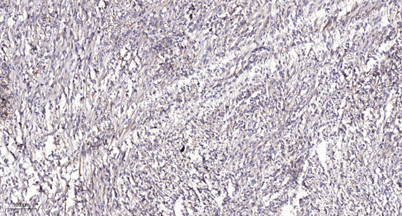
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Colon cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human Colon cancer. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min). -
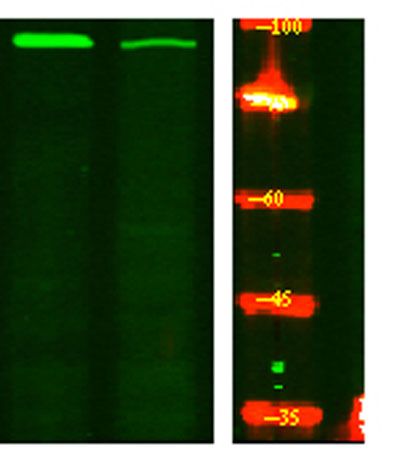
 Western Blot analysis of Hela treated or untreated by LPS lysis, using primary antibody at 1:1000 dilution. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS23920) was diluted at 1:10000
Western Blot analysis of Hela treated or untreated by LPS lysis, using primary antibody at 1:1000 dilution. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS23920) was diluted at 1:10000

 Manual
Manual