

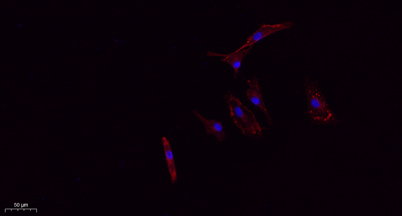




CD63 rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
OverviewPublications(2)
| Product name: | CD63 rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Rat;Mouse; |
| Alternative Names: | CD63; MLA1; TSPAN30; CD63 antigen; Granulophysin; Lysosomal-associated membrane protein 3; LAMP-3; Melanoma-associated antigen ME491; OMA81H; Ocular melanoma-associated antigen; Tetraspanin-30; Tspan-30; CD63 |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | IF: 1:50-200 Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. IHC-p: 1:100-1:300. ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD63. AA range:121-170 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 26,35-65(kD |
| GeneID: | 967 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | P08962 |
| Cellular localization: | Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Lysosome membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Late endosome membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Endosome, multivesicular body . Melanosome . Secreted, extracellular exosome . Cell surface . Also found in Weibel-Palade bodies of endothelial cells (PubMed:10793155). Located in platelet dense granules (PubMed:7682577). Detected in a subset of pre-melanosomes. Detected on intralumenal vesicles (ILVs) within multivesicular bodies (PubMed:21962903). . |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. The encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins. It may function as a blood platelet activation marker. Deficiency of this protein is associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Also this gene has been associated with tumor progression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012], |

 Manual
Manual