






Rad51 rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | Rad51 rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse |
| Alternative Names: | RAD51; RAD51A; RECA; DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1; HsRAD51; hRAD51; RAD51 homolog A |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human RAD51. AA range:281-330 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 42kD |
| GeneID: | 5888 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | Q06609 |
| Cellular localization: | Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Mitochondrion matrix . Chromosome . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Colocalizes with RAD51AP1 and RPA2 to multiple nuclear foci upon induction of DNA damage (PubMed:20154705). DNA damage induces an increase in nuclear levels (PubMed:20154705). Together with FIGNL1, redistributed in discrete nuclear DNA damage-induced foci after ionizing radiation (IR) or camptothecin (CPT) treatment (PubMed:23754376). Accumulated at sites of DNA damage in a SPIDR-dependent manner (PubMed:23509288). Recruited at sites of DNA damage in a MCM9-MCM8-dependent manner (PubMed:23401855). Colocalizes with ERCC5/XPG to nuclear foci in S phase (PubMed:26833090). . |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family. RAD51 family members are highly similar to bacterial RecA and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad51, and are known to be involved in the homologous recombination and repair of DNA. This protein can interact with the ssDNA-binding protein RPA and RAD52, and it is thought to play roles in homologous pairing and strand transfer of DNA. This protein is also found to interact with BRCA1 and BRCA2, which may be important for the cellular response to DNA damage. BRCA2 is shown to regulate both the intracellular localization and DNA-binding ability of this protein. Loss of these controls following BRCA2 inactivation may be a key event leading to genomic instability and tumorigenesis. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009], |
-
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using Rad51 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 cells nucleus extracted by Minute TM Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation kit (SC-003,Inventbiotech,MN,USA).
Western Blot analysis of various cells using Rad51 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 cells nucleus extracted by Minute TM Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation kit (SC-003,Inventbiotech,MN,USA). -
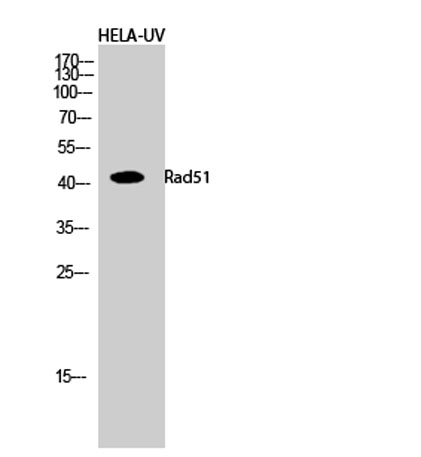
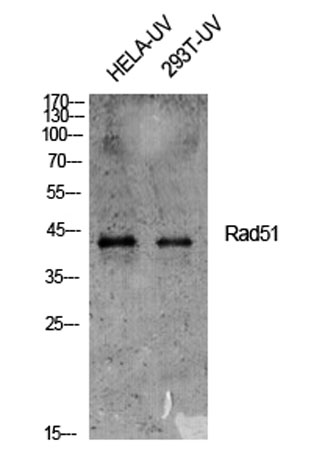
 Western Blot analysis of HELA-UV cells using Rad51 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 cells nucleus extracted by Minute TM Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation kit (SC-003,Inventbiotech,MN,USA).
Western Blot analysis of HELA-UV cells using Rad51 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 cells nucleus extracted by Minute TM Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation kit (SC-003,Inventbiotech,MN,USA). -
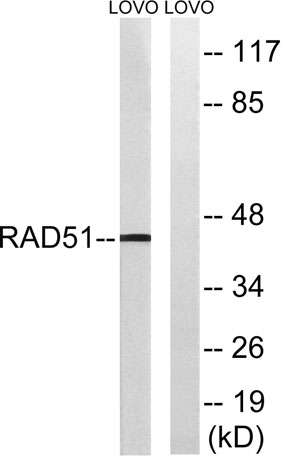
 Western blot analysis of lysates from LOVO cells, using RAD51 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from LOVO cells, using RAD51 Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
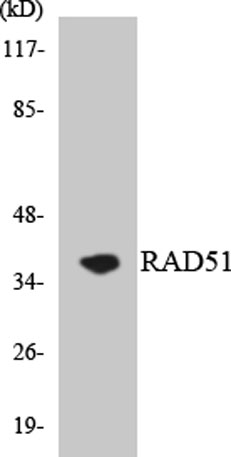
 Western blot analysis of the lysates from HeLa cells using RAD51 antibody.
Western blot analysis of the lysates from HeLa cells using RAD51 antibody.

 Manual
Manual