







PKAα/β cat rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | PKAα/β cat rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | PRKACA; PKACA; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PKA C-alpha; PRKACB; cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit beta; PKA C-beta |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. Immunofluorescence: 1/200 - 1/1000. ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human KAPC A/B. AA range:1-50 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 38kD |
| GeneID: | 5566/5567 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | P17612/P22694 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Nucleus . Mitochondrion . Membrane ; Lipid-anchor . Translocates into the nucleus (monomeric catalytic subunit). The inactive holoenzyme is found in the cytoplasm. Distributed throughout the cytoplasm in meiotically incompetent oocytes. Associated to mitochondrion as meiotic competence is acquired. Aggregates around the germinal vesicles (GV) at the immature GV stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with HSF1 in nuclear stress bodies (nSBs) upon heat shock (PubMed:21085490). .; [Isoform 2]: Cell projection, cilium, flagellum . Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, acrosome . Expressed in the midpiece region of the sperm flagellum (PubMed:10906071). Colocalizes with MROH2B and TCP11 on the acrosome and tail regions in round spermatids and spermatozoa regardle |
| Background: | This gene encodes one of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A, which exists as a tetrameric holoenzyme with two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits, in its inactive form. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits have been identified in humans. cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinase A is important to many cellular processes, including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Constitutive activation of this gene caused either by somatic mutations, or genomic duplications of regions that include this gene, have been associated with hyperplasias and adenomas of the adrenal cortex and are linked to corticotropin-independent Cushing's syndrome. Altern |
-
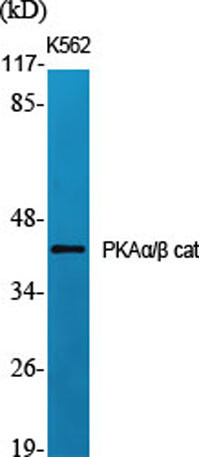
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using PKAα/β cat Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
Western Blot analysis of various cells using PKAα/β cat Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000 -
 Western Blot analysis of Jurkat cells using PKAα/β cat Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000
Western Blot analysis of Jurkat cells using PKAα/β cat Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000 -
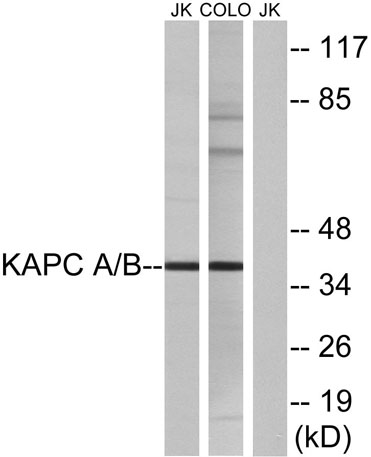
 Western blot analysis of lysates from COLO and Jurkat cells, using KAPC A/B Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from COLO and Jurkat cells, using KAPC A/B Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
 Western blot analysis of the lysates from RAW264.7cells using KAPC A/B antibody.
Western blot analysis of the lysates from RAW264.7cells using KAPC A/B antibody.

 Manual
Manual