



NF-YA rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
-
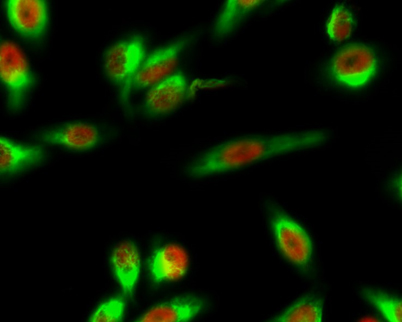 Immunofluorescence analysis of Hela cell. 1,NF-YA Polyclonal Antibody(red) was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). LC3A mouse Monoclonal Antibody(5G10)(green) was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 Catalog:RS3611 was diluted a
Immunofluorescence analysis of Hela cell. 1,NF-YA Polyclonal Antibody(red) was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). LC3A mouse Monoclonal Antibody(5G10)(green) was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 Catalog:RS3611 was diluted a -
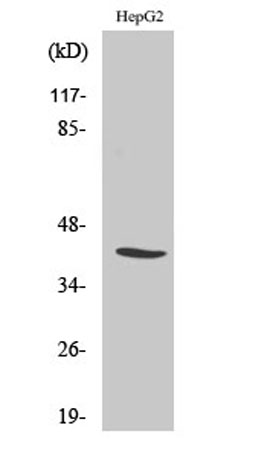 Western Blot analysis of various cells using NF-YA Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000 cells nucleus extracted by Minute TM Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation kit (SC-003,Inventbiotech,MN,USA).
Western Blot analysis of various cells using NF-YA Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:1000 cells nucleus extracted by Minute TM Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fractionation kit (SC-003,Inventbiotech,MN,USA). -
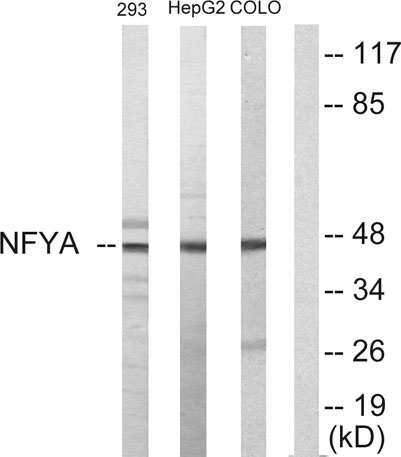 Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2, 293, and COLO205 cells, using NFYA Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2, 293, and COLO205 cells, using NFYA Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human spleen. 1, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 2 Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight.3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human spleen. 1, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 2 Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight.3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 45min).


 Manual
Manual