





LATS1/2 rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | LATS1/2 rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse |
| Alternative Names: | LATS1; WARTS; Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS1; Large tumor suppressor homolog 1; WARTS protein kinase; h-warts; LATS2; KPM; Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS2; Kinase phosphorylated during mitosis protein; Large tumor suppressor ho |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. IHC-p: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1/20000. IF 1:100-300 Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human LATS1/2. AA range:1041-1090 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 130-140kD |
| GeneID: | 9113/26524 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | O95835/Q9NRM7 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle . Midbody . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, spindle pole body . Localizes to the centrosomes throughout interphase but migrates to the mitotic apparatus, including spindle pole bodies, mitotic spindle, and midbody, during mitosis. . |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a putative serine/threonine kinase that localizes to the mitotic apparatus and complexes with cell cycle controller CDC2 kinase in early mitosis. The protein is phosphorylated in a cell-cycle dependent manner, with late prophase phosphorylation remaining through metaphase. The N-terminal region of the protein binds CDC2 to form a complex showing reduced H1 histone kinase activity, indicating a role as a negative regulator of CDC2/cyclin A. In addition, the C-terminal kinase domain binds to its own N-terminal region, suggesting potential negative regulation through interference with complex formation via intramolecular binding. Biochemical and genetic data suggest a role as a tumor suppressor. This is supported by studies in knockout mice showing development of soft-tissue sarcomas, ovarian stromal cell tumors and a high sensitivity to carcinogenic treatmen |
-
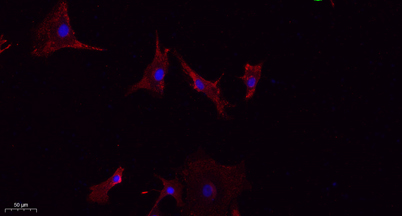
 Immunofluorescence analysis of A549. 1,primary Antibody(red) was diluted at 1:200(4°C overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit IgG (H&L) - Alexa Fluor 594 Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:1000(room temperature, 50min).3, Picture B: DAPI(blue) 10min.
Immunofluorescence analysis of A549. 1,primary Antibody(red) was diluted at 1:200(4°C overnight). 2, Goat Anti Rabbit IgG (H&L) - Alexa Fluor 594 Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:1000(room temperature, 50min).3, Picture B: DAPI(blue) 10min. -
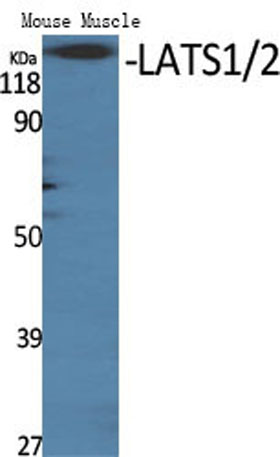
 Western Blot analysis of mouse-mscle cells using LATS1/2 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
Western Blot analysis of mouse-mscle cells using LATS1/2 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 -
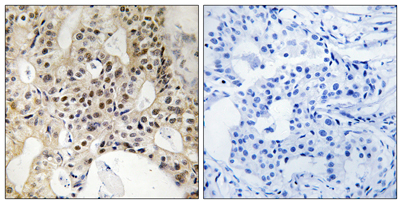
 Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using LATS1/2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma tissue, using LATS1/2 Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
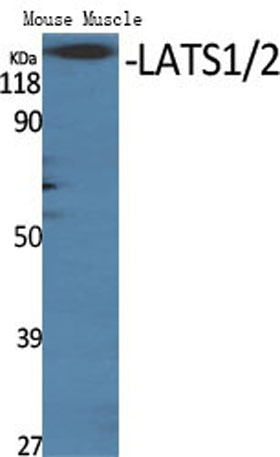
 Western blot analysis of LATS1/2 Antibody
Western blot analysis of LATS1/2 Antibody

 Manual
Manual