





CFTR rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | CFTR rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | CFTR; ABCC7; Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; CFTR; ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 7; Channel conductance-controlling ATPase; cAMP-dependent chloride channel |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. ELISA: 1/5000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human CFTR. AA range:711-760 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 168kD |
| GeneID: | 1080 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | P13569 |
| Cellular localization: | Apical cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Early endosome membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Cell membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Recycling endosome membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Endoplasmic reticulum membrane ; Multi-pass membrane protein . Nucleus . The channel is internalized from the cell surface into an endosomal recycling compartment, from where it is recycled to the cell membrane (PubMed:17462998, PubMed:19398555, PubMed:20008117). In the oviduct and bronchus, detected on the apical side of epithelial cells, but not associated with cilia (PubMed:22207244). In Sertoli cells, a processed product is detected in the nucleus (By similarity). ER stress induces GORASP2-mediated unconventional (ER/Golgi-independent) trafficking of core-glycosylated CFTR t |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MRP subfamily that is involved in multi-drug resistance. The encoded protein functions as a chloride channel and controls the regulation of other transport pathways. Mutations in this gene are associated with the autosomal recessive disorders cystic fibrosis and congenital bilateral aplasia of the vas deferens. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, many of which result from mutations in this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008], |
-
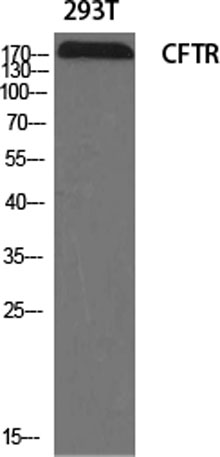
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using CFTR Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000
Western Blot analysis of various cells using CFTR Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000 -
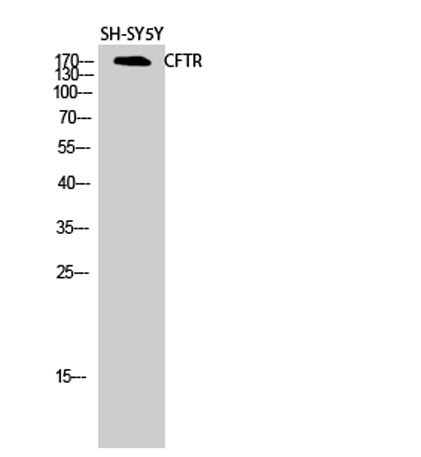
 Western Blot analysis of SH-SY5Y cells using CFTR Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000
Western Blot analysis of SH-SY5Y cells using CFTR Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000 -
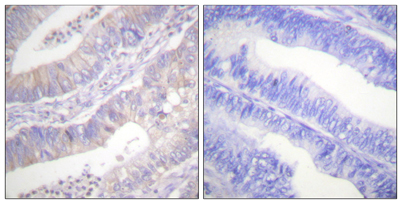
 Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma tissue, using CFTR Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma tissue, using CFTR Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
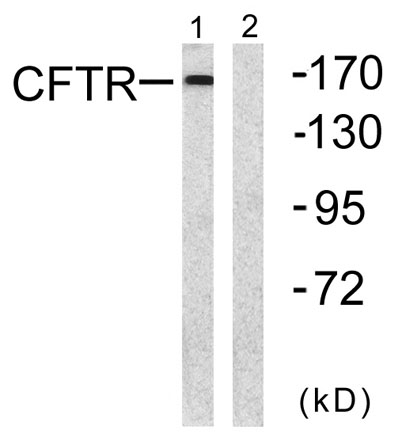
 Western blot analysis of lysates from NIH/3T3 cells, using CFTR Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from NIH/3T3 cells, using CFTR Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.

 Manual
Manual