





DRP1 (phospho-Ser616) rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
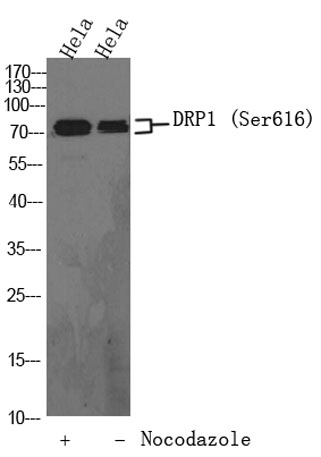
| Product name: | DRP1 (phospho-Ser616) rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | Dynamin-1-like protein (EC 3.6.5.5) (Dnm1p/Vps1p-like protein) (DVLP) (Dynamin family member proline-rich carboxyl-terminal domain less) (Dymple) (Dynamin-like protein) (Dynamin-like protein 4) (Dynamin-like protein IV) (HdynIV) (Dynamin-related protein 1) |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | WB 1:1000-2000 |
| Immunogen: | Synthesized phosho peptide around human DRP1 (Ser616) |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 80kD |
| GeneID: | 10059 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | O00429 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Golgi apparatus. Endomembrane system; Peripheral membrane protein. Mitochondrion outer membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein. Peroxisome. Membrane, clathrin-coated pit . Cytoplasmic vesicle, secretory vesicle, synaptic vesicle membrane . Mainly cytosolic. Recruited by RALA and RALBP1 to mitochondrion during mitosis (PubMed:21822277). Translocated to the mitochondrial membrane through O-GlcNAcylation and interaction with FIS1. Colocalized with MARCHF5 at mitochondrial membrane. Localizes to mitochondria at sites of division. Localizes to mitochondria following necrosis induction. Recruited to the mitochondrial outer membrane by interaction with MIEF1. Mitochondrial recruitment is inhibited by C11orf65/MFI (By similarity). Associated with peroxisomal membranes, partly re |
| Background: | This gene encodes a member of the dynamin superfamily of GTPases. The encoded protein mediates mitochondrial and peroxisomal division, and is involved in developmentally regulated apoptosis and programmed necrosis. Dysfunction of this gene is implicated in several neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease. Mutations in this gene are associated with the autosomal dominant disorder, encephalopathy, lethal, due to defective mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission (EMPF). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013], |

 Manual
Manual