







SHIP-1 (phospho Tyr1021) rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | SHIP-1 (phospho Tyr1021) rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | INPP5D; SHIP; SHIP1; Phosphatidylinositol 3; 4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 1; Inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase of 145 kDa; SIP-145; SH2 domain-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase 1; SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase 1; SHIP-1; |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | WB 1:500-2000; IF/ICC 1:50-200;ELISA 1:2000-20000;IHC-p 1:50-200 |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human SHIP1 around the phosphorylation site of Tyr1021. AA range:987-1036 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 133kD |
| GeneID: | 3635 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | Q92835 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm . Cell membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein . Membrane raft . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton . Membrane ; Peripheral membrane protein . Translocates to the plasma membrane when activated, translocation is probably due to different mechanisms depending on the stimulus and cell type. Translocates from the cytoplasm to membrane ruffles in a FCGR3/CD16-dependent manner. Colocalizes with FC-gamma-RIIB receptor (FCGR2B) or FCGR3/CD16 at membrane ruffles. Tyrosine phosphorylation may also participate in membrane localization. . |
| Background: | This gene is a member of the inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase (INPP5) family and encodes a protein with an N-terminal SH2 domain, an inositol phosphatase domain, and two C-terminal protein interaction domains. Expression of this protein is restricted to hematopoietic cells where its movement from the cytosol to the plasma membrane is mediated by tyrosine phosphorylation. At the plasma membrane, the protein hydrolyzes the 5' phosphate from phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate and inositol-1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate, thereby affecting multiple signaling pathways. The protein is also partly localized to the nucleus, where it may be involved in nuclear inositol phosphate signaling processes. Overall, the protein functions as a negative regulator of myeloid cell proliferation and survival. Mutations in this gene are associated with defects and cancers of the immune system. A |
-
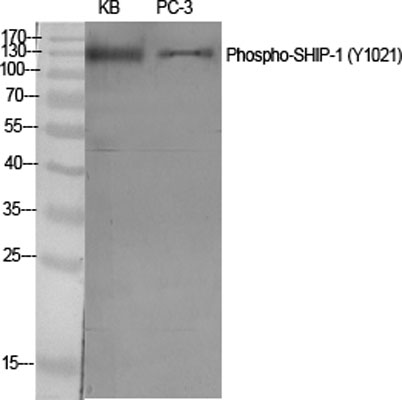
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-SHIP-1 (Y1021) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-SHIP-1 (Y1021) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 -
 Western Blot analysis of KB cells using Phospho-SHIP-1 (Y1021) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500
Western Blot analysis of KB cells using Phospho-SHIP-1 (Y1021) Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:500 -
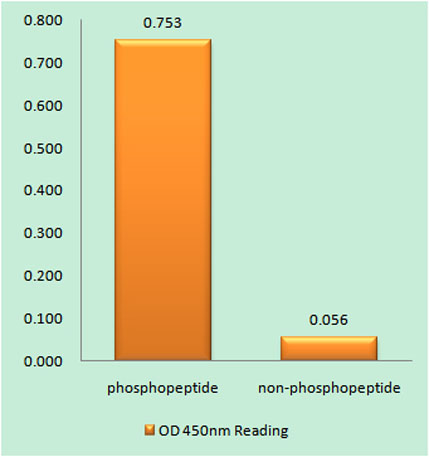
 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using SHIP1 (Phospho-Tyr1021) Antibody
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Phospho-ELISA) for Immunogen Phosphopeptide (Phospho-left) and Non-Phosphopeptide (Phospho-right), using SHIP1 (Phospho-Tyr1021) Antibody -
 Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 cells treated with TNF 200NG/ML 30', using SHIP1 (Phospho-Tyr1021) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from HepG2 cells treated with TNF 200NG/ML 30', using SHIP1 (Phospho-Tyr1021) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.

 Manual
Manual